
1. A large, scratched boulder is found in a mixture of
unsorted, smaller sediments forming a hill in central New
York State. Which agent of erosion most likely transported
and then deposited this boulder?
1) wind 3) ocean waves
2) a glacier 4) running water
2. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram
below, which shows ocean waves approaching a shoreline.
A groin (a short wall of rocks perpendicular to the
shoreline) and a breakwater (an offshore structure) have
been constructed alone the beach. Letters A, B, C, D, and E
represent locations in the area.
At which location will the beach first begin to widen due to
sand deposition?
1) A 3) C
2) B 4) E
3. The major landscape regions of the United States are
identified chiefly on the basis of
1) similar surface characteristics
2) similar climatic conditions
3) nearness to major mountain regions
4) nearness to continental boundaries
4. The diagram below shows a cross section of a portion of
Earth's crust. Altitude is shown in meters above sea level.
This landscape region is best classified as an eroded
1) plain 3) domed mountain
2) plateau 4) folded lowland
5. Which landscape feature is most likely to be formed from a
bedrock layer that is resistant to erosion?
1) coastal plain 3) valley
2) glacial moraine 4) cliff
6. Which diagram represents a plateau landscape?
1)
2)
3)
4)
7. Which kind of stream pattern would most likely be found
on the type of landscape shown in the diagram?
1)
3)
2)
4)
8. The landscape of northeastern New York State was formed
mainly by
1) mountain building and glacial erosion
2) faulting and volcanic activity
3) changes in the water level of Lake Ontario
4) erosion of Devonian sedimentary bedrock by rivers
Landscape Development Review

Base your answers to questions
9
and
10
on the three maps below, which show the ice movement and changes at the ice front of an alpine glacier
from the years 1874 to 1882. Points A, B. C, D, and E represent the positions of large markers placed on the glacial ice and left there for a period
of eight years.
9. The changing positions of markers A, B. C, D, and E show that the glacial ice is
1) slowly becoming thicker 3) gradually shifting northward
2) forming smaller crystals 4) moving fastest near the middle
10. Which statement best describes the changes happening to this glacier between 1874 and 1882?
1) The ice front was advancing, and the ice within the glacier was advancing.
2) The ice front was advancing, and the ice within the glacier was retreating.
3) The ice front was retreating, and the ice within the glacier was advancing.
4) The ice front was retreating, and the ice within the glacier was retreating.
Landscape Development Review

Base your answers to questions
11
and
12
on the map below. Arrows on the map show the location and orientation of glacial striations on the
surface bedrock. Dark shading shows the location of large moraines (glacial deposits).
11. The striations indicate that the movement of glacial ice was toward the
1) northeast and northwest 2) northeast and southwest 3) southeast and northwest 4) southeast and southwest
12. How were the striations made?
1) Frost action cracked the bedrock during the ice age.
2) Rocks at the bottom of the glaciers were dragged over the bedrock.
3) Particles carried by winds scratched the bedrock during the ice age.
4) Particles carried by glacial meltwater eroded the bedrock.
Landscape Development Review

Base your answers to questions
13
through
15
on the map and cross section below. The map shows the shapes and locations of New York State’s
11 Finger Lakes and the locations of some major glacial deposits (moraines) left behind by the last ice age. The cross section shows surface
elevations, valley depths, and water depths of the Finger Lakes.
13. Which statement provides the best evidence that New York State’s Finger Lakes formed as a result of continental glaciation?
1) The lake surfaces are above sea level. 3) The lakes are partially filled with sorted beds of sediment.
2) The lakes fill long, narrow, U-shaped valleys. 4) The lakes are surrounded by sharp, jagged peaks and ridges.
14. The general shape of the Finger Lakes and the pattern of moraine deposits found across Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and New York are
evidence that the continental glacier was advancing from
1) south to north 2) north to south 3) east to west 4) west to east
15. In which New York State landscape region are the Finger Lakes located?
1) Hudson-Mohawk Lowlands 2) Erie-Ontario Lowlands 3) Allegheny Plateau 4) the Catskills
16. Which landscape region separates the Adirondack
Mountains from the Catskills?
1) Taconic Mountains
2) Tug Hill Plateau
3) Hudson-Mohawk Lowlands
4) Champlain Lowlands
17. During which period of geologic history was the surface
bedrock of the Catskills deposited?
1) Cambrian 3) Devonian
2) Pleistocene 4) Triassic
Landscape Development Review

18. Shaded areas on the diagrams below show the part of New York State that was covered by glacial ice during the last ice age.
The best inference that can be made from these diagrams is that this glacial ice
1) was about 1 mile thick at New York City 3) moved more slowly than the glaciers of earlier ice ages
2) advanced and retreated more than once 4) changed the shape of Lake Ontario
19. Which graph best represents the range of particle sizes that can be carried by a glacier?
1)
2)
3)
4)
20. What type of landscape region is located at 42º30' N and
76º W?
1) coastal lowland 3) plateau
2) mountainous area 4) plain
21. Which city is located in a landscape region showing
distorted and altered bedrock structure?
1) Old Forge 3) Syracuse
2) Niagara Falls 4) Binghamton
Landscape Development Review

22. The cross sections below show a three-stage sequence in the development of a glacial feature.
Which glacial feature has formed by the end of stage 3?
1) kettle lake 2) finger lake 3) drumlin 4) parallel scratches
23. The map below shows some features along an ocean shoreline.
In which general direction is the sand being moved along this shoreline by ocean (long–shore) currents?
1) northeast 2) southeast 3) northwest 4) southwest
24. Which map shows the stream drainage pattern that usually
develops on the surface of horizontal rock layers?
1)
3)
2)
4)
25. At which latitude and longitude in New York State would a
salt mine in Silurian-age bedrock most likely be located?
1) 41° N 72° W 3) 44° N 74° W
2) 43° N 77° W 4) 44° N 76° W
26. Which New York landscape region is composed primarily
of Cretaceous through Pleistocene unconsolidated
sediments?
1) Champlain Lowlands
2) Erie-Ontario Lowlands
3) Hudson-Mohawk Lowlands
4) Atlantic Coastal Lowlands
27. The surface bedrock of the Tug Hill Plateau landscape
region is mostly composed of
1) igneous rock of Silurian age
2) sediments of Tertiary age
3) metamorphic rock of Precambrian age
4) sedimentary rock of Ordovician age
28. Which New York State landscape feature was formed
primarily as a result of glacial deposition?
1) Adirondack Mountains
2) Hudson-Mohawk Lowlands
3) Tug Hill Plateau
4) Long Island
Landscape Development Review

29. Which stream-drainage pattern most likely developed on
the surface of a newly formed volcanic mountain?
1)
2)
3)
4)
30. The surface bedrock of the Hudson Highlands is best
described as
1) Middle Proterozoic gneisses and quartzites
2) unconsolidated Cretaceous gravels, sands, and clays
3) Pennsylvanian conglomerates and sandstones
4) Devonian limestones and shales
31. Landscape regions are best identified by their
1) fossils and rock age
2) latitude and climate
3) elevation and bedrock structure
4) soil composition and particle size
32. Which sequence shows the order in which landscape
regions are crossed as an airplane flies in a straight course
from Albany, New York, to Massena, New York?
1) plateau →
plain →
mountain
2) plateau →
mountain →
plain
3) plain →
mountain →
plain
4) mountain →
plain →
plateau
33. The map below shows the ancient location of evaporating
seawater, which formed the Silurian-age deposits of rock
salt and rock gypsum now found in some New York State
crustal bedrock.
Within which two landscape regions are these large rock
salt and rock gypsum deposits found?
1) Hudson Highlands and Taconic Mountains
2) Tug Hill Plateau and Adirondack Mountains
3) Erie-Ontario Lowlands and Allegheny Plateau
4) the Catskills and Hudson-Mohawk Lowlands
34. The generalized geologic cross section below represents
part of New York and Vermont.
A major landscape region boundary is shown at location
1) A 3) C
2) B 4) D
35. If the rate of erosion in a particular landscape on the Earth's
surface increases and the uplifting forces remain constant,
the elevation of that landscape will
1) decrease 3) remain the same
2) increase
36. Which change is most likely to occur in a landscape region
that is uplifted rapidly by folding?
1) The climate will become warmer.
2) The stream drainage patterns will change.
3) The composition of the bedrock will change.
4) The hillslopes will become less steep.
Landscape Development Review
37. The table below shows characteristics of three landscape regions, X, Y, and Z.
Which terms, when substituted for X, Y, and Z, best complete the table?
1) X = mountains, Y = plains, Z = plateaus 3) X = plains, Y = plateaus, Z = mountains
2) X = plateaus, Y = mountains, Z = plains 4) X = mountains, Y = plateaus, Z = plains
38. The list below shows characteristics that vary from place to
place on Earth.
a Radioactive substances
b Bedrock structures
c Duration of insolation
d Hill slopes
e Stream patterns
f Atmospheric composition
Observations and measurements of which three
characteristics would be most useful in describing
landscapes?
1) a, b,and c 3) b, d,and e
2) b, c,and f 4) d, e,and f
39. If weathering and erosion were the only geological
processes taking place on the Earth, most landscapes would
be characterized by
1) low relief and gentle gradients
2) low relief and steep gradients
3) high relief and gentle gradients
4) high relief and steep gradients
40. One characteristic used to classify landscape regions as
plains, plateaus, or mountains is
1) type of soil
2) amount of stream discharge
3) weathering rate
4) underlying bedrock structure
41. An environmental scientist needs to prepare a report on the
potential effects that a proposed surface mine in New York
State will have on the watershed where the mine will be
located. In which reference materials will the scientist find
the most useful data with which to determine the
watershed’s boundaries?
1) topographic maps 3) tectonic plate maps
2) geologic time scales 4) planetary wind maps
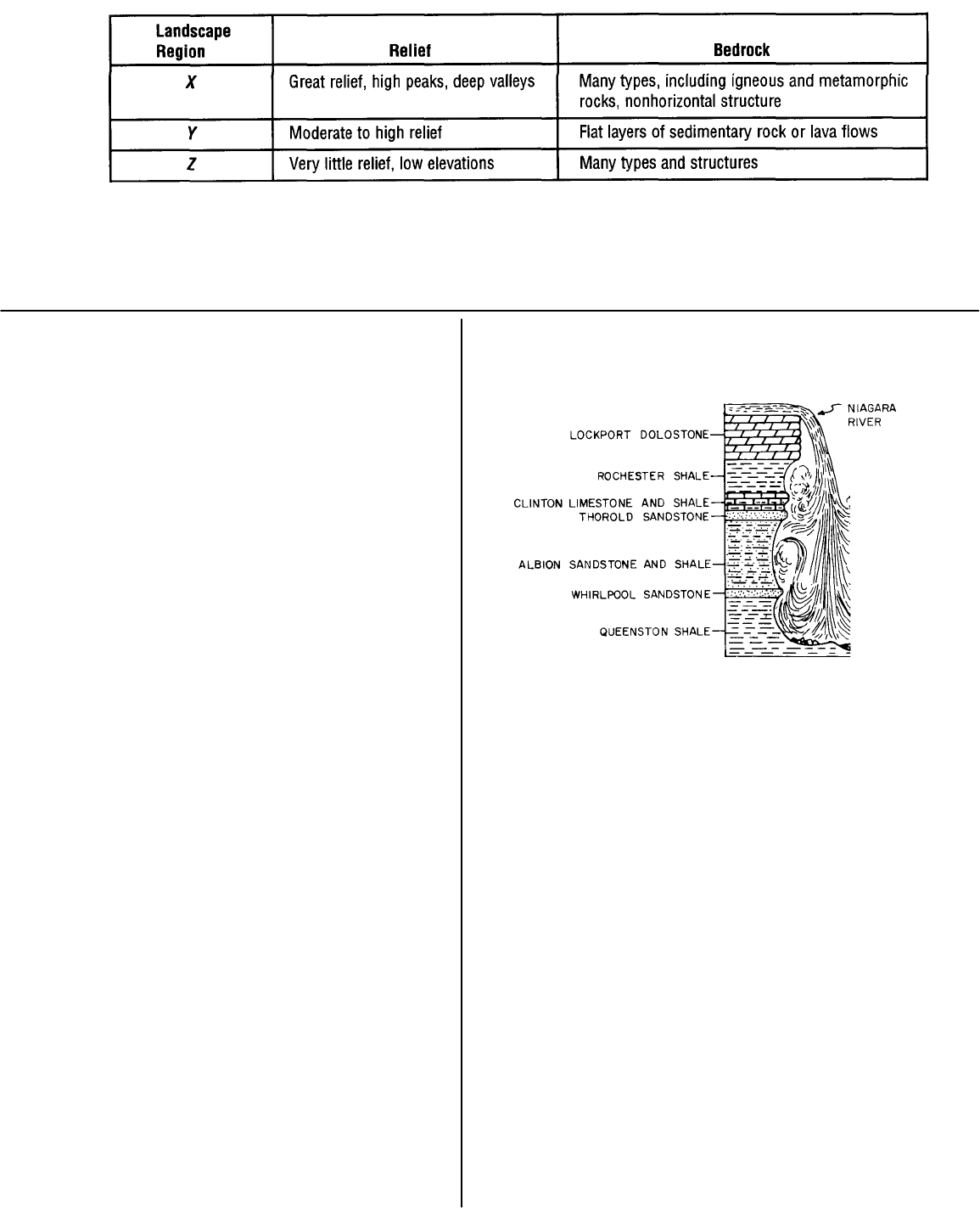
42. The diagram below shows a geologic cross section of the
rock layers in the vicinity of Niagara Falls in western New
York State.
Which statement best explains the irregular shape of the
rock face behind the falls?
1) The Lockport dolostone is an evaporite.
2) The Clinton limestone and shale contain many fossils.
3) The Thorold sandstone and the whirlpool sandstone
dissolve easily in water.
4) The Rochester and Queenston shale and the Albion
sandstone and shale are less resistant to erosion than
the other rock layers.
Landscape Development Review

43. The sequence of bedrock cross sections below represents the same landscape region over a period of geologic time.
This sequence best represents
1) an arid region that experienced mostly uplifting forces 3) a humid region that experienced mostly uplifting forces
2) an arid region that experienced mostly erosional forces 4) a humid region that experienced mostly erosional forces
44. The diagram below represents a cross section of the
bedrock and land surface in part of Tennessee. The dotted
lines indicate missing rock layers.
Which statement is best supported by the diagram?
1) Rocks are weathered and eroded evenly.
2) Folded rocks are more easily weathered and eroded.
3) Deposits of sediments provide evidence of erosion.
4) Climate differences affect the amount of erosion.
45. The diagrams below represent geologic cross sections from
two widely separated regions.
The layers of rock appear very similar, but the hillslopes
and shapes are different. These differences are most likely
the result of
1) volcanic eruptions 3) soil formation
2) earthquake activity 4) climate variations
Landscape Development Review

Answer KeyAnswer Key
1. 2
2. 2
3. 1
4. 2
5. 4
6. 2
7. 1
8. 1
9. 4
10. 3
11. 4
12. 2
13. 2
14. 2
15. 3
16. 3
17. 3
18. 2
19. 3
20. 3
21. 1
22. 1
23. 2
24. 1
25. 2
26. 4
27. 4
28. 4
29. 1
30. 1
31. 3
32. 3
33. 3
34. 2
35. 1
36. 2
37. 4
38. 3
39. 1
40. 4
41. 1
42. 4
43. 2
44. 2
45. 4
