
Wi-Fi
Security
1

Agenda
Overview of Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi Communication
Security Challenges with Wi-Fi
Demonstration: Evil Twin Attack
Encryption
Wi-Fi Security Protocols
Safeguard Yourself
Questions
2

What is Wi-Fi?
• Wi-Fi is a wireless networking
technology, based on the IEEE 802.11
standards, that allows devices such as
computers (laptops and desktops),
mobile devices (smart phones and
wearables), and other equipment
(security systems, smart home devices,
cars, TVs, printers, video cameras, etc.)
to interface with a Local Area Network
(LAN) and/or the Internet. (CISCO)
3

How Does WiFi
Communication
Work?
• Wi-Fi devices use radio waves in
the 2.4GHz or 5GHz band to
transmit and receive data over the
air.
• In essence, Wi-Fi Devices are
Radio Transceivers
• Modern Wi-Fi Devices have the
capability to use either 2.4GHz or
5GHz (dual band) to achieve a
connection.
4
Frequency
Bands
2.4GHz
5GHz
Pros
• Longer Range
•
Better
transmission
through walls
• Faster speeds
•
Supports
more devices
• Less prone to
interference
Cons
•
Subject to
interference
with other
technology
operating on a
similar
frequency
•
Short Range
•
Does not
travel well
through
obstacles.

How Does WiFi Communication Work?
5
• The transmission and
receiving of digital
information over the air is
accomplished by a process
called RF Modulation.
• RF modulation transforms
digital data, such as binary
1s and 0s representing an e-
mail message, from the
network into an RF signal
suitable for transmission
through the air.
Hello World!
1001000 1100101 1101100 1101100 1101111 100000
1010111 1101111 1110010 1101100 1100100 100001
Modulator
Amplifier
Antenna

Security Challenges with Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi Piggybacking:
Unauthorized connection to a
Wi-Fi network.
• Commonly occurs in areas
where residences are in
close proximity.
• Open Wi-Fi networks are
most susceptible
• War Driving: A specific
kind of piggybacking where
someone drives around and
maps out where unsecured
networks are around a city
or neighborhood.
6

Security Challenges with Wi-Fi
Evil Twin Attack: An
Adversary impersonates a
public Wi-Fi access point
and convinces a victim to
connect to the malicious
AP. The adversary can use
this connection to intercept
network traffic or harvest
credentials.
7
SSID: BestEastern_Hotel
Adversary
Victim
SSID: BestEastern_Hotel_Guest

Security Challenges with Wi-Fi
Wireless Sniffing: Takes
advantage of unencrypted
Wi-Fi communication to
collect network traffic that
may contain information
like access credentials, PII,
and other information
8
Unsecure Home
Network
The
Adversary
1001000 1100101 1101100 1101100 1101111
100000 1010111 1101111 1110010 1101100
1100100 100001
The Victim
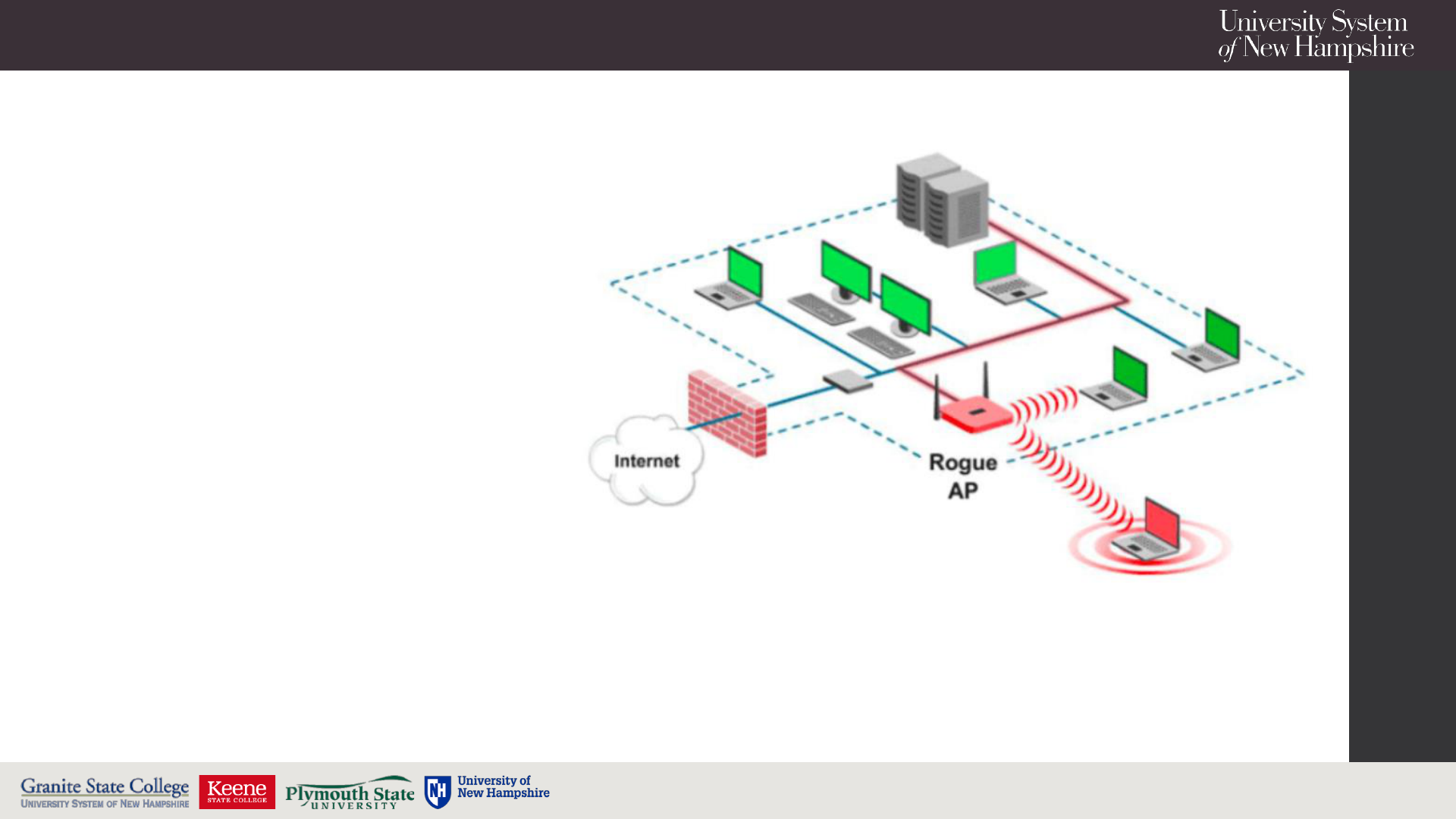
Security Challenges with Wi-Fi
Rogue Access Points: A
rogue access point is an AP
that is connected to a
company’s physical
network infrastructure but
is not under that
company’s administrative
control. (Cisco)
• Could be an Insider
• Could be an Adversary
9

Adversary Motivations
• Why should you protect yourself against
these types of attacks.?
People are actively trying to hack
you!
• Financial Gain
• Recognition and Achievement
• Insider Threats
• Political Motivation – “Hactivism”
• State Actors
• Espionage
10

Demonstration
• The following video is going to depict
what an Evil Twin attack might look like
from the victim and hackers perspective.
• For this demonstration I used a Wi-Fi
Pineapple in a controlled environment for
educational purposes.
• This particular Wi-Fi Pineapple is a
penetration testing tool, designed to test
the security of an organization.
• Warning! The following section
contains tools, tactics, and
techniques that can only be lawfully
used for education and professional
purposes. Using these methods for
any other purpose is punishable
under federal and state law!
11

Wi-Fi Security Protocols
• Open/Unsecured Wi-Fi
• “When wireless devices in a
network are "open" or unsecured,
they're accessible to any Wi-Fi-
enabled device, such as a computer
or smartphone, that's within range
of their wireless signals.” (Cisco)
• “Using open or unsecured networks
can be risky for users and
organizations. Adversaries using
internet-connected devices can
collect users' personal information
and steal identities, compromise
financial and other sensitive
business data, "eavesdrop" on
communications, and more.” (Cisco)
12
The Lack of a “Lock” indicator suggests
that this network is open and quite
possibly not secure.

Wireless Security Protocols- Cryptosystem
13
• Encryption is the process of converting or scrambling data and information into an unreadable, encoded version
that can only be read with authorized access.
• Four basic components of encryption:
• (1) plaintext (non-encrypted message),
• (2) encryption algorithm (works like a locking mechanism to a safe)
• (3) key (works like the safe's combination)
• (4) ciphertext (produced from plaintext message by encryption key).
Encrypted (Ciphertext)
Unencrypted (Plaintext) Message
Decrypted (Plaintext) Message
Key
(dfk49dk4jx0fk5)
Key
(dfk49dk4jx0fk5)
Bob
Access Point
Encryption
Decryption

Wireless Security Protocols- WEP
14
WEP: Wired Equivalent Privacy
• Developed in the late 1990s
• Depreciated in 2004
• Issues:
• Limited Key Length
• Bits of data containing key information are repeated given
enough traffic
• Should never be used – “crackable” in under one minute.

Wireless Security Protocols- WPA1
15
WPA1 (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
• Released in 2003
• Depreciated in 2009
• Used same encryption algorithm as WEP (RC4)
• Uses Temporal Key Integration Protocol in for
implementing keys, which was an improvement over WEP
• Additional protection with Message Integrity Checks
• Issues:
• Suffered from some of the same vulnerabilities as WEP,
and limitations in Message Integrity Checking, and
therefore should be AVOIDED

Wireless Security Protocols- WPA2
16
WPA2 (WI-Fi Protected Access)
• Released in 2004
• Still commonly used
• Uses the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). The same
type of encryption used by the US Government.
• Issues:
• In 2017 researchers found that vulnerabilities in the
authentication process could lead to key-reuse.
• Vulnerable to brute force attacks

Wireless Security Protocols- WPA3
17
WPA3 (WI-Fi Protected Access)
• Announced in 2018
• Longer key length, and better implementation of keys
• Protection against brute force attacks
• Opportunistic Wireless Encryption: supports encryption
on open networks. (coffee shops, hotel wireless, airports.)
• Vulnerabilities/Issues:
• Unpatched clients can be tricked to downgrade to
WPA2,
• Not yet available everywhere (can be costly for large
organizations to implement.

Securing Your Home Wi-Fi Network
18
• 1. Change your default Wi-Fi
SSID and hide your network.
(turn off network broadcasting)
• 2. Use a strong and unique
password/passphrase greater than
20 characters
• 3.Use the strongest encryption
available on your Wi-Fi router and
devices (WPA2,WPA3)
• 4. Keep your router’s firmware up
to date.
• 5. Change your routers default
admin credentials
Fun SSID Names:
No More Mister Wifi
Bandwidth on the Run
Obi-WLan Kenobi
LAN BEFORE TIME
The Silence of the
LANs
Benjamin FrankLAN
Theodore Routervelt

Safeguard Yourself While Using Public Wi-Fi
19
• 1. Use a VPN
• 2. Consider using your mobile phone
as a Wi-fi hotspot.
• 3. Disable Auto-connect
• 4. Use HTTPS sites over HTTP
• 5. Use Different passwords for
different accounts.
• 6. Limit the use of sites that require
credentials and contain account
details.
• 7. Implement MFA everywhere
possible!

Recap:
Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology designed for mobility and
convenience.
Wi-Fi devices are radios
Wi-Fi networking has unique security challenges
Employ encryption methods to protect your data as it travels in the
air
There are many best practices you can employ to secure your
network and yourself.
Thank You!
20

Works Cited
• “What Is Wi-Fi? - Definition and Types.” Cisco, Cisco, 22 Dec. 2021,
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/wireless/what-is-
wifi.html#:~:text=Wi%2DFi%20is%20a%20wireless,to%20interface%20with%20the%20Internet.
• “WIFI Networking: Radio Wave Basics.” Network Computing, 10 Jan. 2019,
https://www.networkcomputing.com/wireless-infrastructure/wifi-networking-radio-wave-basics.
• National Security Agency Cybersecurity Report. https://www.nsa.gov/portals/75/documents/what-we-
do/cybersecurity/professional-resources/ctr-uefi-defensive-practices-guidance.pdf. “Security Tip (ST05-
003).”
• Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency CISA, https://www.cisa.gov/tips/st05-
003#:~:text=What%20are%20the%20risks%20to%20your%20wireless%20network%3F,Surfing%20...%207
%20Theft%20of%20Mobile%20Devices%20.
• Kaspersky. “WEP, WPA, WPA2 and WPA3: Differences and Explanation.” Usa.kaspersky.com, 21 Sept.
2021, https://usa.kaspersky.com/resource-center/definitions/wep-vs-wpa.
• Kalitut, Not Available. “Rogue AP - Fake Access Points.” KaliTut, 16 June 2020, https://kalitut.com/rogue-
ap-fake-access-points/.
Thank You!
21

Questions?
22
